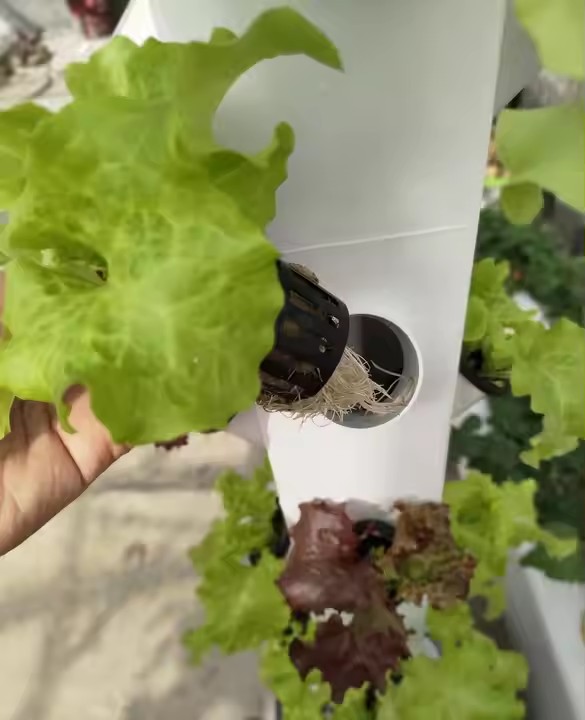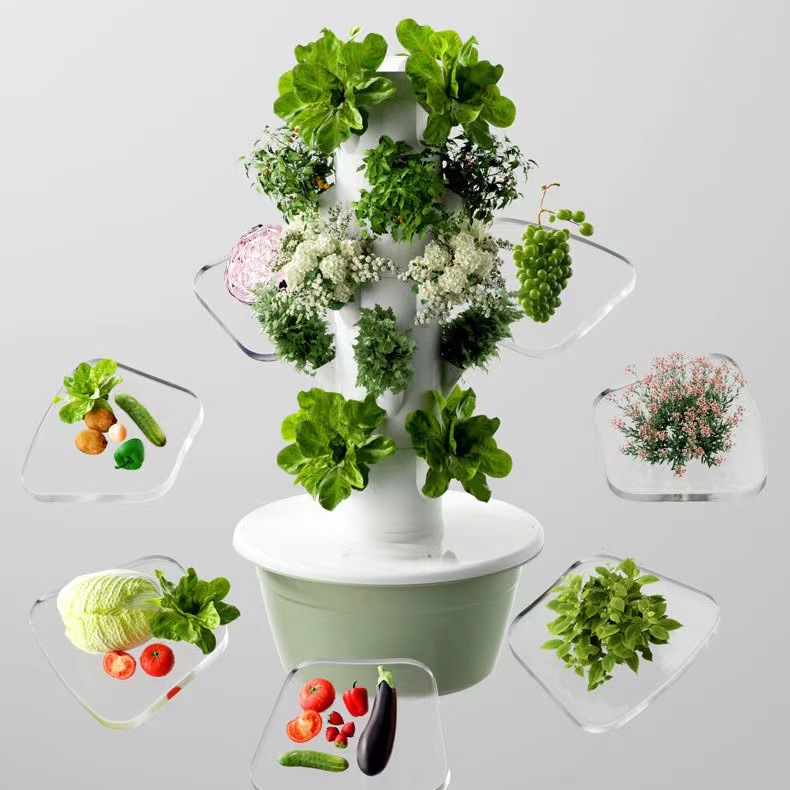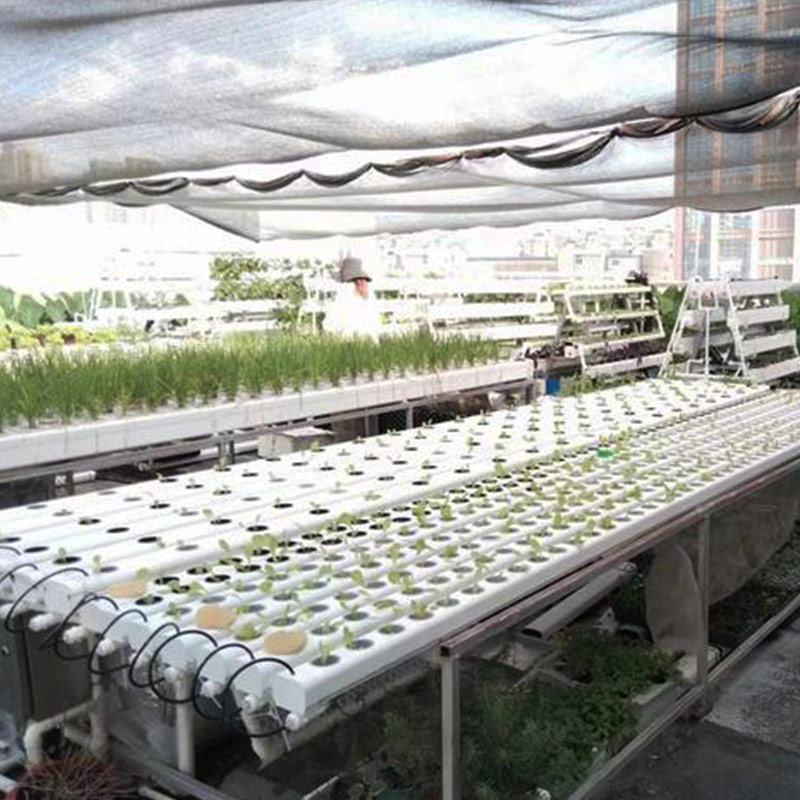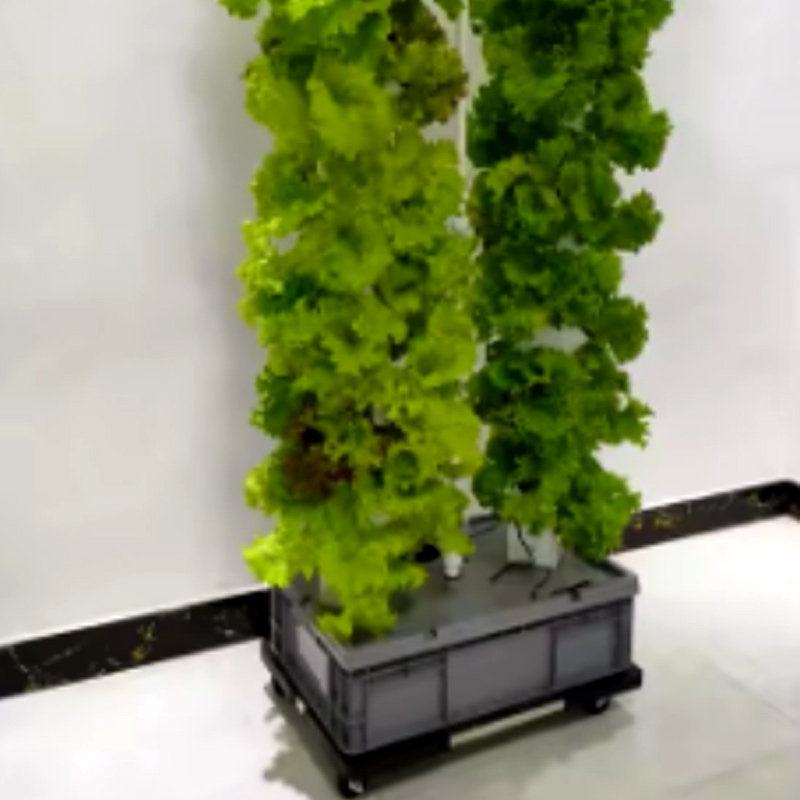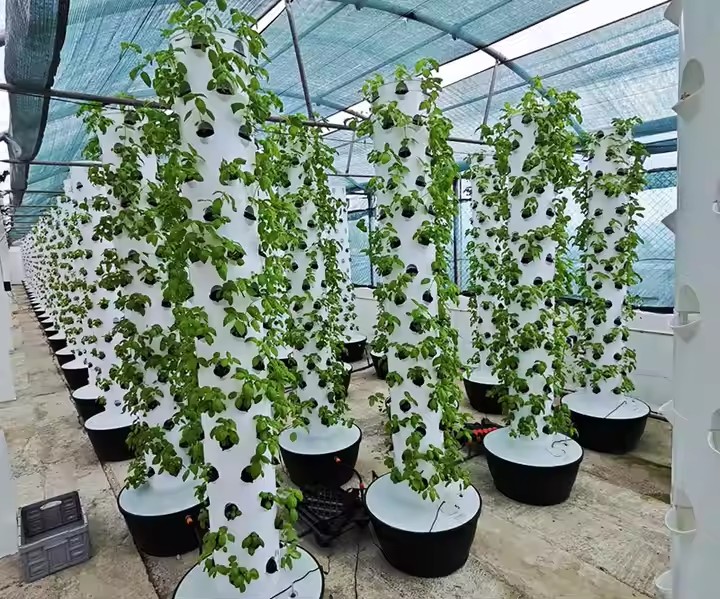
A-shaped hydroponic planting system is an efficient vertical farming design that maximizes growing space while minimizing footprint. Its triangular structure provides dual-sided planting surfaces, making it ideal for leafy greens, herbs, and strawberries.
A-shaped Hydroponic Planting System
1. Introduction to A-shaped hydroponic planting system
The A-Frame hydroponic system represents a revolutionary approach to vertical farming, combining space efficiency with high-yield production. Characterized by its distinctive triangular structure, this design provides dual growing surfaces at optimal angles for light penetration and easy harvesting. Originally developed for commercial lettuce production, A-Frame systems now accommodate everything from strawberries to medicinal herbs.
Why Choose A-shaped hydroponic planting system?
Space Optimization: Grows 2-3x more plants per square foot than flat beds
Ergonomic Design: 45-60° angle reduces labor strain during maintenance
Adaptability: Functions with NFT, drip irrigation, or aeroponic systems
Climate Resilience: Protected growing environment for year-round production
2. Historical Development of A-shaped hydroponic planting system
1970s: Early prototypes emerge in Dutch greenhouse operations
1990s: Commercial adoption for lettuce in Japan and California
2010s: Integration with LED lighting and automation technologies
Present: Standard in urban vertical farms and research facilities
3. Scientific Principles of A-shaped hydroponic planting system
The A-Frame's effectiveness stems from three core scientific advantages:
Light Penetration
The 45-60° angle ensures:92% light absorption efficiency (vs 68% in flat beds)
Even distribution across all plant levels
Reduced shading between plants
Gravity-Assisted Drainage
Natural water flow prevents stagnation
30% less pump energy required than vertical towers
Microclimate Control
Air circulates freely through open center
Temperature variance <2°C across structure
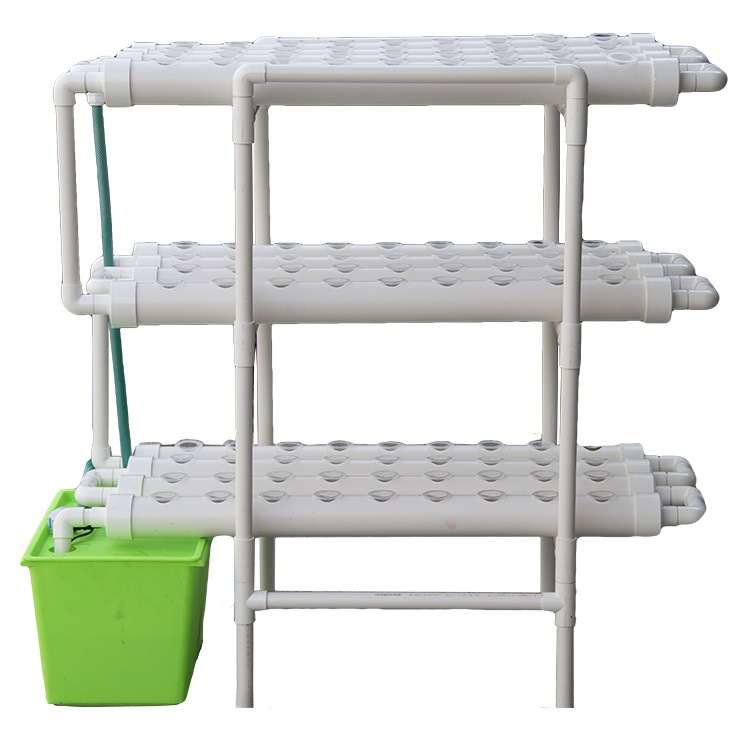
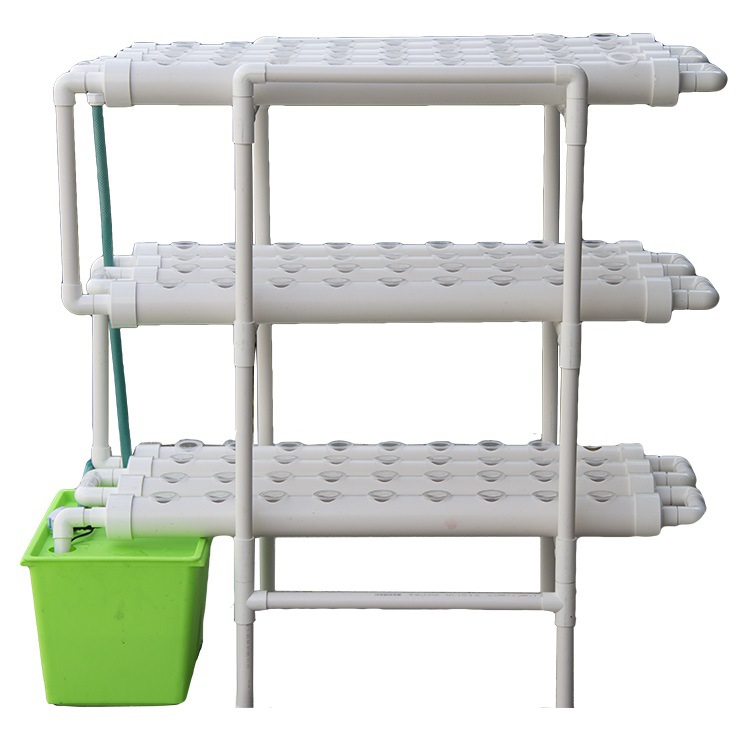
4. System Components
| Component | Purpose | Recommended Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Frame Structure | Structural support | Powder-coated aluminum or UV-resistant PVC |
| Growing Channels | Plant housing | Food-grade PVC pipes (3-6" diameter) or gutters |
| Irrigation System | Nutrient delivery | Drip emitters (0.5 GPH) or NFT channels |
| Reservoir | Nutrient storage | 20-100 gallon capacity |
| Water Pump | Circulation | 400-800 GPH submersible |
| Lighting System | Supplemental light | Full-spectrum LEDs (50W per linear foot) |
5. Types of A-Frame Systems
A. NFT (Nutrient Film Technique) A-Frames
Best for: Leafy greens, herbs
Flow rate: 1-2 liters per minute
Advantage: Minimal media needed
B. Drip Irrigation A-Frames
Best for: Strawberries, peppers
Media: Coco coir or perlite
Advantage: Precise nutrient control
C. Hybrid Aeroponic A-Frames
Best for: High-value crops
Technology: Root misting every 3-5 minutes
Advantage: 40% faster growth rates
6. Growing Media Comparison
| Media Type | A-Frame Suitability | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clay Pebbles | Excellent | Reusable, good drainage | Heavy when wet |
| Coconut Coir | Good | Sustainable, moisture-retentive | Requires buffering |
| Rockwool | Fair | Sterile, consistent | Non-biodegradable |
| Perlite | Good | Lightweight, inexpensive | Can compact over time |
7. Plant Selection Guidelines
Top Performing Crops:
Leafy Greens: Lettuce (all varieties), kale, arugula
Herbs: Basil, cilantro, mint
Fruiting Plants: Strawberries, cherry tomatoes
Flowers: Petunias, marigolds (for companion planting)
Plants to Avoid:
Large root vegetables (carrots, potatoes)
Vining plants (unless pruned aggressively)
Tall crops (corn, sunflowers)
8. Lighting Strategies
Natural Light Optimization
Orient frames north-south for even sun exposure
6+ hours direct sunlight required outdoors
Artificial Lighting Solutions
LED Strip Configuration: 30W per linear foot
Light Schedule: 14-16 hours daily for greens
PAR Requirements: 200-400 μmol/m²/s for vegetative growth
9. Structural Engineering
Critical Design Parameters:
Angle: 50° optimal for light/water distribution
Base Width: 24-36 inches for stability
Height: 6-8 feet maximum for easy access
Load Capacity: 5 lbs per linear foot (when wet)
Material Options:
PVC: Affordable (1.50 per linear foot)
Aluminum: Durable (5 per linear foot)
Stainless Steel: Commercial-grade ($8+ per linear foot)
10. Step-by-Step Construction
Materials Needed:
(4) 8' 2x4 lumber or PVC pipes
(2) 4' crossbeams
10' of 4" PVC gutter
400 GPH water pump
20-gallon reservoir
Assembly Instructions:
Construct A-frame with 50° angle using metal brackets
Install growing channels at 12" vertical spacing
Connect irrigation lines with 6" emitter spacing
Test water flow (adjust slope as needed)
Install plants in net pots with media














