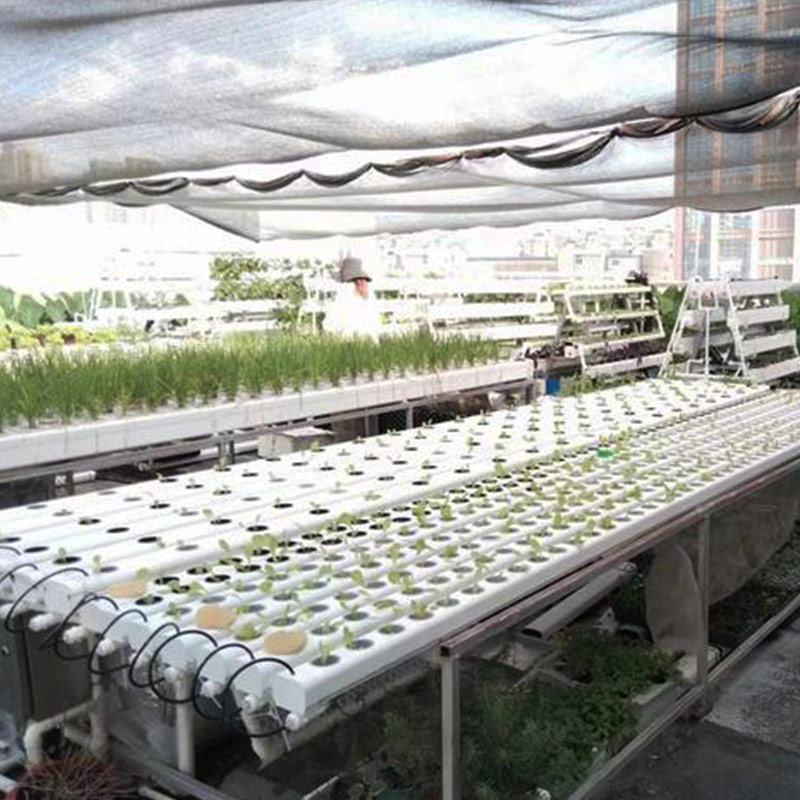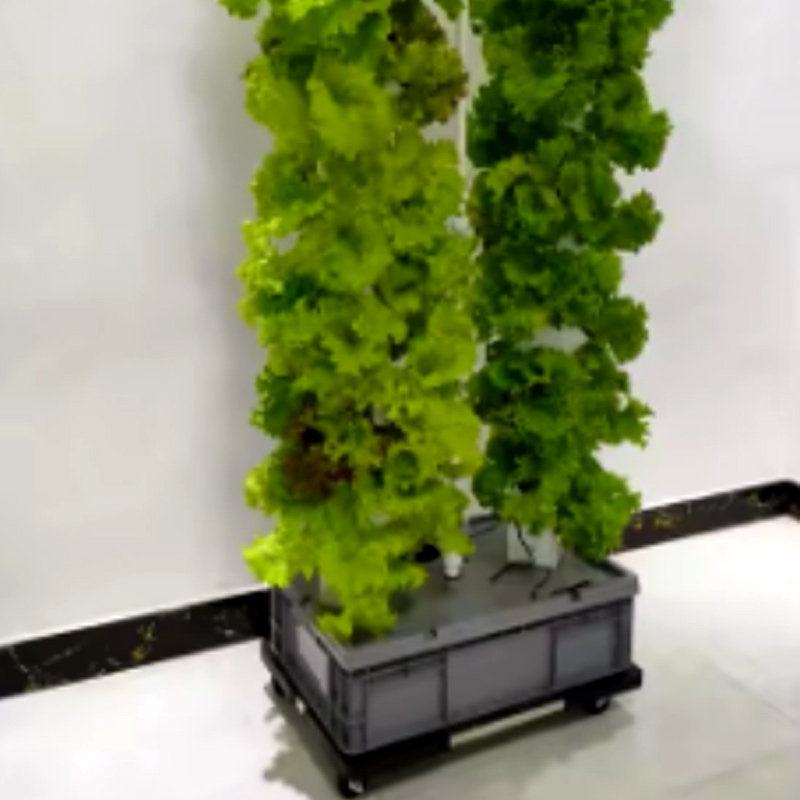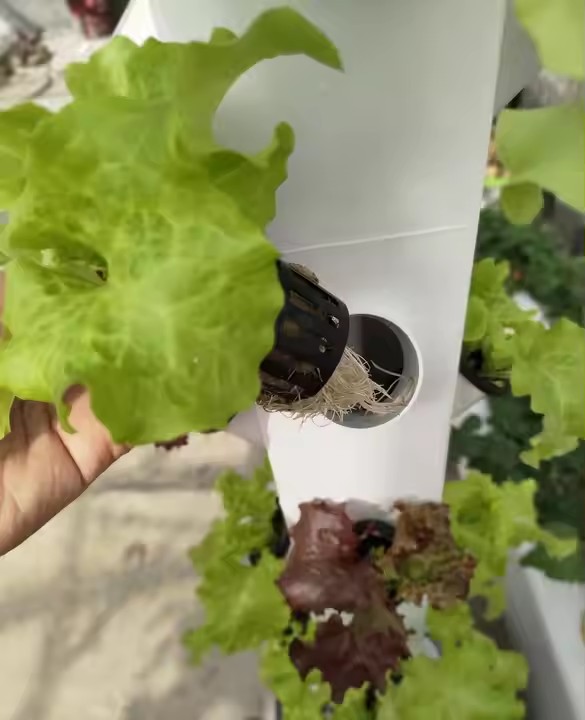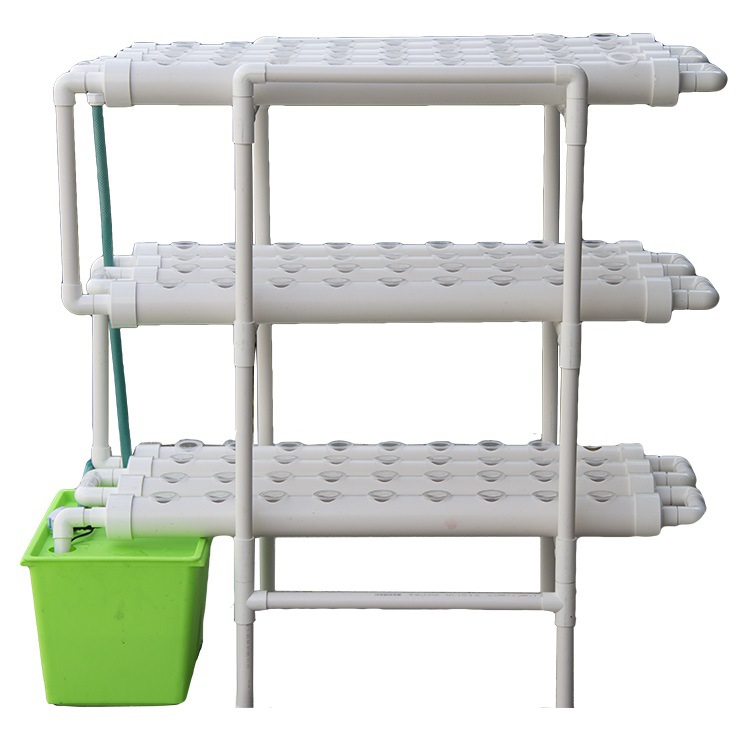
hydroponic cultivation greenhouse combines protected agriculture with soilless growing technology to optimize crop production. These structures enable year-round cultivation of high-quality vegetables, herbs, and fruits by precisely controlling climate, nutrients, and light.
Hydroponic Cultivation Greenhouse
1. Introduction to Hydroponic Greenhouses
Hydroponic cultivation greenhouses represent the pinnacle of controlled environment agriculture (CEA), combining protected growing structures with soilless cultivation techniques. These advanced facilities enable growers to:
Achieve year-round production regardless of external climate
Obtain 3-10 times higher yields than field production
Reduce water usage by 85-95% compared to soil farming
Eliminate herbicide use and minimize pesticides
Produce consistent, high-quality crops meeting strict market standards
Modern hydroponic greenhouses range from small backyard structures to multi-acre commercial facilities, all sharing the common principle of optimizing every growth factor - light, temperature, humidity, CO₂, and nutrients.
2. Scientific Principles of hydroponic cultivation greenhouse
Hydroponic greenhouses leverage several core scientific concepts:
A. Photosynthesis Optimization
Maintain optimal light intensity (400-800 μmol/m²/s)
Control CO₂ levels (800-1200 ppm during daylight)
Regulate temperature (day: 70-80°F, night: 60-70°F)
B. Root Zone Management
Dissolved oxygen >6 ppm in nutrient solutions
Precise pH control (5.5-6.5 for most crops)
Nutrient balance tailored to growth stages
C. Microclimate Control
VPD (Vapor Pressure Deficit) management
Airflow optimization to prevent disease
Thermal buffering strategies
3. Types of hydroponic cultivation greenhouse
| System Type | Best For | Water Use | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| NFT Channels | Leafy greens | Very Low | Medium |
| Deep Water Culture | Herbs, lettuce | Low | Low |
| Ebb & Flow | Starter plants | Medium | Medium |
| Drip Irrigation | Tomatoes, cucumbers | Medium | High |
| Aeroponics | High-value crops | Very Low | Very High |
4. Structural Components of hydroponic cultivation greenhouse
A. Framework Materials
Galvanized Steel: Commercial standard (30+ year lifespan)
Aluminum: Lightweight, rust-proof (higher cost)
PVC: Budget option (5-8 year lifespan)
B. Covering Materials
| Material | Light Transmission | Durability | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | 92% | 25+ years | $$$$ |
| Polycarbonate | 88% | 10-15 years | $$$ |
| Polyethylene Film | 85% | 3-5 years | $ |
C. Foundation Options
Concrete Perimeter: Permanent installations
Ground Anchors: Temporary or seasonal structures
Raised Beds: For small-scale operations
5. Climate Control Systems of hydroponic cultivation greenhouse
A. Temperature Regulation
Heating: Boilers, heat pumps, or geothermal
Cooling: Ventilation, shade cloths, evaporative pads
Thermal Screens: Energy-saving insulation
B. Humidity Management
Fogging Systems: For arid climates
Dehumidifiers: For tropical regions
Ventilation: Automated roof vents
C. CO₂ Enrichment
Optimal Levels: 800-1200 ppm
Sources: Burners, tanks, or fermentation
Timing: Daylight hours only
6. Lighting Strategies of hydroponic cultivation greenhouse
A. Natural Light Optimization
Orientation: East-west for even distribution
Glazing: Anti-reflective coatings
Light Diffusion: Prismatic panels
B. Supplemental Lighting
| Light Type | Efficiency | Lifespan | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| LED | 2.5 μmol/J | 50,000 hrs | Full-cycle growth |
| HPS | 1.7 μmol/J | 24,000 hrs | Flowering/fruiting |
| CMH | 2.0 μmol/J | 20,000 hrs | Vegetative growth |
C. Photoperiod Control
Vegetative Stage: 16-18 hours light
Flowering Stage: 12 hours light
Automated Controllers: Sunrise/sunset simulation
7. Hydroponic Subsystems of hydroponic cultivation greenhouse
A. Nutrient Delivery Systems
Recirculating: 90% water savings
Drain-to-Waste: For salt-sensitive crops
Hybrid Systems: Combine multiple methods
B. Monitoring Equipment
pH/EC Controllers: Maintain optimal ranges
Water Chillers: Prevent root diseases
ORP Meters: Track solution freshness
8. Automation Technologies of hydroponic cultivation greenhouse
A. Environmental Controls
Climate Computers: Integrate all sensors
Weather Stations: Predictive adjustments
Mobile Alerts: Real-time monitoring
B. Irrigation Automation
Moisture Sensors: Prevent over/under watering
Fertigation Dosers: Precise nutrient delivery
Self-Cleaning Filters: Reduce maintenance
9. Crop Selection Guide
High-Profit Greenhouse Crops:
Leafy Greens: Butterhead lettuce, kale, arugula
Herbs: Basil, cilantro, mint
Vegetables: Tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers
Berries: Strawberries, raspberries
Flowers: Orchids, roses, chrysanthemums
Crop-Specific Requirements:
| Crop | Temp (°F) | EC (mS/cm) | Days to Harvest |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lettuce | 60-70 | 1.2-1.8 | 28-35 |
| Tomatoes | 70-80 | 2.5-3.5 | 60-90 |
| Basil | 75-85 | 1.8-2.2 | 35-42 |
10. Commercial Economics
Startup Costs (1-Acre Greenhouse):
Structure: 300,000
Systems: 200,000
Annual Operating: 100,000
Revenue Potential:
Leafy Greens: $500,000+/acre/year
Tomatoes: $1M+/acre/year
Cannabis: $3M+/acre/year (licensed markets)
11. Environmental Benefits
Water Conservation: 90% less than field farming
Land Efficiency: 10-20x yield per acre
Carbon Footprint: 60% reduction vs imported produce
Pesticide Reduction: 95% less than conventional
12. Future Innovations
AI-Powered Optimization: Machine learning for climate control
Vertical Integration: Stacked growing systems
Renewable Energy: Solar-powered operations
Robotic Harvesting: Automated picking/packing
Conclusion
Hydroponic cultivation greenhouses represent the future of sustainable agriculture, offering unprecedented control over growing conditions while dramatically reducing environmental impact. Whether you're a small-scale grower or commercial operator, these systems provide:
✔ Year-round production in any climate
✔ Higher quality and yields than field growing
✔ Significant resource savings (water, land, energy)
✔ Reliable income streams from premium crops
With proper planning and management, hydroponic greenhouses can deliver exceptional returns on investment while contributing to global food security.















